Entertainment
AI-Powered TV Production: Unleashing Creativity with Showrunner
Showrunner, an AI-powered TV production platform, allows users to create personalised episodes with simple text prompts, revolutionising the way we consume television.
Published
12 months agoon
By
AIinAsia
TL;DR
- Showrunner, an AI-powered platform, enables AI-powered TV production.
- Users are able to create personalised TV episodes with simple text prompts.
- The platform handles writing, voice acting, animation, and sound effects, making TV production accessible to all.
- Showrunner’s initial lineup features 10 animated shows, with ‘Exit Valley’ currently available for alpha users.
The Rise of AI in Television: Introducing Showrunner
Imagine creating your own TV show with just a few clicks. Thanks to advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), this dream is becoming a reality. Showrunner, a new platform developed by The Simulation (formerly Fable Studio), is transforming the way we watch and create television. This innovative platform allows users to generate TV episodes using simple text commands, handling everything from writing and voice acting to animation and sound effects.
How Does Showrunner Work?
Showrunner operates on a text-to-episode format. Users input a 10- to 15-word prompt, and the platform generates scenes and episodes ranging from two to 16 minutes. The AI-powered system manages dialogue, voice acting, editing, camera angles, character development, and plot progression, creating a seamless viewing experience.
Showrunner’s Lineup: What Shows Can You Watch or Create?
Showrunner offers a variety of animated shows spanning different genres and styles. Here’s a sneak peek into some of the shows available:
- Exit Valley: A satirical take on tech entrepreneurs, with the first episode now available for alpha users.
- What We Leave Behind: An anime family drama about two orphans in Sim Francisco.
- Ikiru Shinu: is a gripping horror anime set in a post-apocalyptic world.
- Sim Francisco: An anthology series exploring the lives of various characters.
- Pixels: A family comedy featuring AI-enabled devices.
To join the Showrunner waitlist and gain early access, visit the official website and enter your email address.
The Impact of AI-Generated TV Shows
AI tools like Showrunner are not yet revolutionising the entertainment industry, but they provide an exciting glimpse into the future of AI-powered TV production. While these tools can generate content based on prompts, they currently struggle to match human creativity. However, AI could become a valuable tool for brainstorming and generating initial story ideas, potentially transforming the creative landscape.
Comment and Share:
What do you think about AI-generated TV shows? Would you create your own episode using Showrunner? Share your thoughts below and don’t forget to subscribe for updates on AI and AGI developments in Asia. Join our community at AI in Asia to engage with like-minded individuals and stay informed about the latest trends.
You may also like:
- The Dark Side of AI Influencers
- From an AI-powered Baby Cry Translator to Personal Assistant robots, AI Takes Over CES 2024
- To learn more about AI video creation, tap here to check out Sora.
Author
Discover more from AIinASIA
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
You may like
Entertainment
How Adobe’s AI Is Transforming 2D Animation Forever
Adobe Animate and After Effects are reshaping 2D animation with AI. Explore how AI-driven lip-sync, motion interpolation, and smart rigging are revolutionising the industry.
Published
1 month agoon
April 30, 2025By
AIinAsia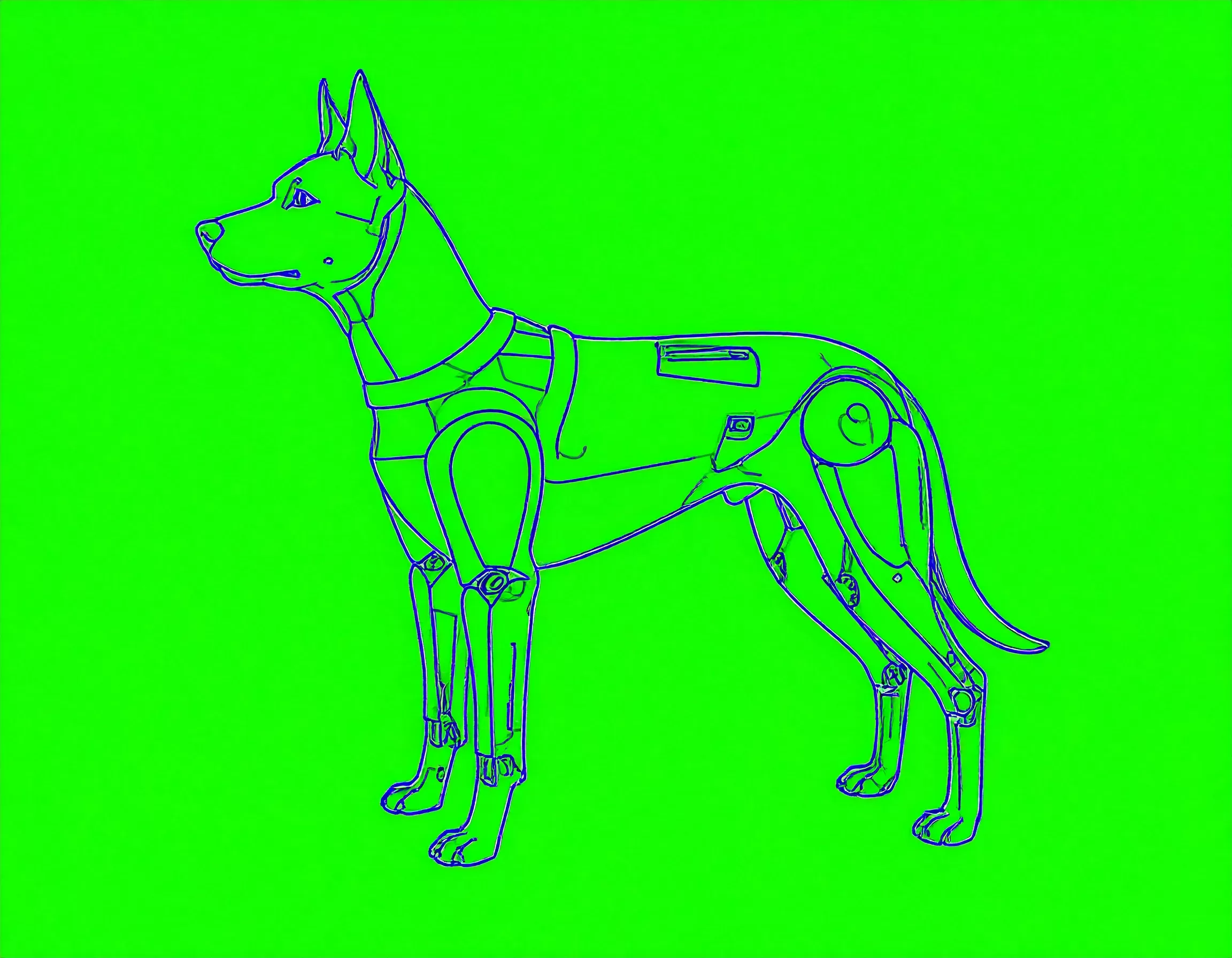
TL;DR — 30-second takeaway
- Adobe Animate and After Effects now integrate advanced AI features like Auto Lip-Sync, motion interpolation, and smart rigging, dramatically speeding up 2D animation workflows.
- AI is helping animators automate complex tasks like dialogue syncing, movement smoothing, and character rigging across different styles.
- The future of 2D animation will be faster, more accessible, and creativity-driven — levelling the playing field for indie creators and studios alike.
The Revolution of 2D Animation: Adobe’s AI Breakthrough
Artificial Intelligence has changed how we work, live — and now, how we animate.
While 2D animation has long been seen as a labour of love involving painstaking frame-by-frame artistry, Adobe’s new AI integrations are turning that process on its head. With tools like Adobe Sensei powering the latest versions of Animate and After Effects, animators are gaining powerful shortcuts that don’t sacrifice creativity or quality.
Let’s dive into how AI is breathing new life into 2D animation.
Using AI to Optimise Animation Production
Gone are the days when syncing a character’s lips to dialogue took days of manual work. Thanks to Auto Lip-Sync in Adobe Animate, AI can now automatically match mouth movements to voices, saving animators hours — if not days — per project. Even better, the results look natural and expressive, without laborious manual adjustments.
Motion interpolation is another game-changer. Adobe’s AI-enhanced algorithms smooth out transitions between poses, allowing for more dynamic and fluid animation with far less manual tweaking. New animators can now create complex movement sequences without mastering every technical nuance of traditional techniques.
Even pacing — often the hardest part to master — has been made easier. AI can now intelligently analyse movement patterns and adjust timings automatically, enhancing the natural flow of character actions.
Smart Rigging: The Most Transformative Leap Yet
Ask any animator: rigging — building the structure beneath a character’s movement — is one of the most demanding stages of animation.
Enter AI smart rigging.
Adobe’s tools now allow animators to automate rig creation, apply rigs across multiple characters, and even adjust rigs for different artistic styles — all with minimal manual input. Instead of redrawing entire rigs for every background character, artists can reuse and adapt base models in a few clicks.
Adobe Character Animator takes it a step further. With real-time motion capture using facial recognition, creators can animate characters simply by speaking and moving in front of a webcam. Neural networks in After Effects now predict motion paths more intelligently than ever, making movements look astonishingly natural with less effort.
The result? Animators can now spend more time on storytelling and less time on technical heavy lifting.
An Industry Poised for a New Era
We’re only scratching the surface of what AI in 2D animation can do.
With the combination of AI-driven animation tools and generative design platforms, we’re heading towards a future where small teams — or even solo creators — can produce animations that rival big-budget studio productions.
The impact is already being felt: independent creators are winning major awards (see Flow at the Oscars), and animation studios are accelerating production schedules like never before.
The real revolution isn’t just in faster animations — it’s in democratising creativity itself.
What do YOU think?
If AI removes the technical barriers in animation, will artistic creativity finally be the only true differentiator between success and failure? Let us know in the comments below.
You may also like:
Author
Discover more from AIinASIA
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Entertainment
How AI-Assisted Music Helped Resurrect The Beatles To Grammy Nominations
“Now and Then” by The Beatles is the first AI-assisted song nominated for Grammy awards.
Published
7 months agoon
November 13, 2024By
AIinAsia
TL;DR
- “Now and Then” by The Beatles is the first AI-assisted song nominated for Grammy awards, including Record of the Year and Best Rock Performance.
- AI technology, specifically “stem separation,” was crucial in isolating John Lennon’s vocals from a low-quality cassette, enabling the completion of the song.
- The song’s release in November 2023 generated global excitement and emotional responses from fans, highlighting AI’s role in preserving artistic legacies.
The Beatles Final Encore and Grammy History
In a remarkable combination of heritage and innovation, “Now and Then” by The Beatles has achieved the distinction of being the first AI-assisted song nominated for Grammy awards, signifying an important development in both the music industry and the influence of technology on creative fields.
Recognised for Record of the Year and Best Rock Performance, this track not only displays the enduring appeal of The Beatles but also emphasises AI’s ability to revive and maintain artistic legacies for future audiences.
The Background of “Now and Then”: Recovering a Forgotten Track
1. The Late-70s Demo and Lennon’s Heritage:
Originally an unfinished recording by John Lennon, “Now and Then” was never finalised due to technical difficulties. Captured on a low-quality cassette, Lennon’s vocals could not be separated from the piano backing, and his intentions for the song remained unclear, with just fragments of lyrics and melody guiding the band years later.
2. Abandonment and Resurgence Attempts:
In the mid-1990s, Paul McCartney and the rest of The Beatles tried to finish the song but eventually abandoned the project because of sound quality concerns and possible differences in artistic vision. With advancements in machine learning, filmmaker Peter Jackson revived this aspiration in 2021, employing sophisticated audio isolation techniques to extract Lennon’s vocals and breathe new life into the song. This technology, developed for Jackson’s Get Back documentary, proved essential in revealing the band’s original artistic intentions.
The Impact of AI on “Now and Then” as AI-assisted music
1. AI-Driven Audio Isolation:
The turning point emerged from an AI-enhanced method known as “stem separation,” a state-of-the-art technique designed to isolate different audio components. In “Now and Then”, the AI effectively separated Lennon’s voice from the piano, background sounds, and low-frequency noise. This process created a clear and distinct vocal track that could harmoniously integrate with recordings from McCartney, Starr, and Harrison’s archives.
2. Audio Restoration Focused on Enhancement:
Unlike generative AI, which creates new materials, the AI employed in this process concentrated solely on refining Lennon’s initial recordings. By enhancing and isolating the pre-existing audio, it kept Lennon’s genuine voice intact, honouring both the song’s legacy and its artistic authenticity. Producer Giles Martin emphasised the goal of enhancing Lennon’s voice without producing artificial elements, guaranteeing that the vocal delivery felt genuine and historically accurate.
3. AI Restoration Versus Traditional Methods:
Previously, in audio restorations, engineers depended on manual equalisation and noise reduction methods, which often compromised sound quality. In contrast, AI provided unmatched accuracy, striking a balance between fidelity and authenticity. The technology’s capacity to identify and extract complex audio layers enabled the production team to revive the song with a clarity that traditional techniques could not match.
The Last Beatles Recording: Creation and Release
1. Contributions from All Four Members of The Beatles:
“Now and Then” brings together all four members of The Beatles, creating a musical connection across generations. Along with Lennon’s vocals, McCartney’s bass, Starr’s drumming, and Harrison’s previously recorded guitar pieces merge into a final version that captures the essence of a true Beatles song. The contributions of each member were thoughtfully blended, resulting in a track that respects both their original spirit and their individual roles.
2. Premiere and Immediate Reaction:
Released in November 2023, “Now and Then” generated important global excitement, not only for its nostalgic value but also for the way it bridged the past and present through technology. It resonated as a heartfelt farewell, eliciting strong emotional responses from fans who found comfort in the song’s enduring melody and lyrics.
Grammy Nominations: A New Chapter for AI in Music
1. Establishing Grammy Milestones with AI:
The nominations for Record of the Year and Best Rock Performance signify the first instance that an AI-enhanced work has achieved this level of acknowledgement, opening doors for future AI-assisted projects. Competing against leading contemporary artists like Beyoncé, Taylor Swift, and Billie Eilish, The Beatles have returned to prominence, once more challenging creative limits even in Grammy qualifications.
2. Grammy Policies on AI and Human Creativity:
While the Recording Academy restricts the extent to which AI can be involved, this nomination is consistent with Grammy rules that allow AI to be used as a supportive tool rather than serving as the main creator. This nomination recognises that AI, when applied with care, can enhance human craftsmanship instead of replacing it, indicating new opportunities for the music industry as AI-supported work becomes increasingly prevalent.
Public and Critical Reaction: Emotional and Technological Impact
1. The Emotional Connection to Fans:
Numerous fans shared powerful emotional responses, recounting how “Now and Then” invoked memories of Lennon, Harrison, and earlier moments associated with The Beatles’ music. The song’s thoughtful nature generated a feeling of finality, moving listeners who sensed that they were receiving a last message from the band. Social media was filled with fans sharing their experiences of how the song brought forth strong memories and ties to their personal lives.
2. Musical Praise and Mixed Reactions:
Critics applauded the song’s evocative tune and production quality, although opinions were split regarding its contemporary production style. While some listeners enjoyed the daring modern sound, others felt it either leaned too much on McCartney’s influence or lost the authenticity that characterised earlier Beatles tracks. The inclusion of AI sparked a discussion over whether this piece could genuinely be classified as a Beatles song or if it strayed too close to a McCartney creation.
3. Ethical and Artistic Concerns:
Both critics and fans questioned the song’s genuineness, with some expressing concerns that AI-assisted tracks could undermine artistic integrity. The ethical conversation focused on whether the utilisation of AI in this way respects or distorts Lennon’s original vision, particularly considering Harrison’s disreported fondness for the song. Nevertheless, this debate also positioned “Now and Then” as a technological achievement, encouraging a conversation about AI’s capability to safeguard legacies.
Breaking New Ground in AI-Assisted Music: AI and The Beatles’ Legacy
1. An Authentic Technological Triumph:
The involvement of AI in “Now and Then” presents a future in which technology can assist rather than change musical craftsmanship. By assisting precise vocal separation, AI has enabled “Now and Then” to connect with audiences as a genuine Beatles song rather than as a synthetic production. The narrative surrounding this song also emphasises how AI can be used to preserve the authenticity of historical works, providing fresh insights into cherished artists.
2. Legacy, Nostalgia, and Artistic Responsibility:
As The Beatles make Grammy history with “Now and Then”, the song emphasises the details of employing AI within legacy music. This release demonstrates how, with thoughtful application, AI can rejuvenate memories without compromising authenticity, enriching The Beatles’ narrative in a manner that feels both innovative and reflective.
Looking Forward: Future Projects and Ethical Debates
1. Possibilities for More AI-Restored Works:
This release paves the way for future endeavours, where AI could potentially restore other unfinished tracks or archival content. However, as technology advances further, the ethical concerns raised by “Now and Then” will likely shape decisions about whether and how AI should be integrated into artists’ legacies.
2. AI in Modern Music Production:
The application of AI in “Now and Then” acts as a model for how AI could support the creation of new music while preserving artistic intention. Its success is expected to motivate other artists and estates to examine how technology can connect the past to the present, and what limits might be established to maintain authenticity throughout the process.
Old Rockers Meet New Technological Innovation with The Beatles
“Now and Then” stands as an important milestone, blending innovation with nostalgia and technology with tradition. In its pursuit of Grammy recognition, the song is a testament to the capability of AI to enrich human creativity, ushering in a new chapter in music history.

As The Beatles are honoured once again in February 2025, “Now and Then” could be recalled as both a homage to their legacy and an indicator of music’s AI-enhanced future.
You can listen to the music video on YouTube by tapping here
Join the Conversation
What are your thoughts on the future of AI in music and its potential to revive and maintain artistic legacies? We’d love to hear your opinions and experiences. Don’t forget to subscribe for updates on AI and AGI developments and share your comments below. Subscribe here.
You may also like:
- AI Music Generator: Creating Songs from Text Prompts
- AI Music Revolution: Suno Fights Back Against Record Labels
- How AI Solves the ‘Cocktail Party Problem’
Author
Discover more from AIinASIA
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Entertainment
An AI Thanksgiving: How Technology is Impacting Your Tradition
How AI is transforming American Thanksgiving traditions from personalised recipes to smarter travel and shopping experiences.
Published
7 months agoon
November 3, 2024By
AIinAsia
TL;DR:
- AI-driven recipes personalise Thanksgiving meals, catering to dietary needs and adding fresh flavours.
- Smart travel apps help families navigate the holiday rush with real-time updates and optimised routes.
- Virtual gatherings feel more connected with AI-enhanced video calls, VR experiences, and accessible features.
- Personalised shopping recommendations and smarter inventory management simplify Black Friday for consumers.
A New Twist on Thanksgiving Traditions
As Thanksgiving approaches in the United States, millions prepare for a holiday steeped in tradition. It’s a day marked by food, family, and gratitude—but this year, technology is adding a new layer to how these traditions unfold. With AI entering more homes and routines, Thanksgiving is evolving beyond the table to include intelligent recipes, virtual gatherings, and a smarter shopping experience. So, how is AI reshaping this traditional holiday in our digital age?
AI at the Thanksgiving Table: Beyond Basic Recipes
Thanksgiving dinner is iconic, from roast turkey to pumpkin pie. AI-driven platforms like ChatGPT and other recipe apps are now helping hosts plan and personalise these traditional dishes. Imagine needing a last-minute substitution or adapting a favourite recipe to fit new dietary preferences—AI can help adjust ingredients, cook times, and even offer cultural twists on classic dishes.
Not only does AI bring convenience, but it also enhances creativity in the kitchen. For families eager to try something new, AI can suggest recipes from diverse cultures or even create “fusion” dishes that blend Thanksgiving’s flavours with global ingredients. It’s a subtle but profound shift, transforming Thanksgiving meals into more inclusive experiences that reflect the diversity around the table.
Holiday Travel Made Smarter with AI
Thanksgiving is one of the busiest travel periods in the US, and AI-powered travel apps are taking on a vital role. From real-time route adjustments based on traffic patterns to automated updates on flight delays, AI helps families navigate the Thanksgiving rush with fewer headaches.
Platforms like Google Maps and Waze, both AI-enhanced, analyze traffic data to reroute travelers around congestion, helping families arrive in time for the holiday feast. AI-powered weather forecasting tools also provide precise updates, aiding those traveling long distances. By simplifying holiday travel logistics, AI reduces stress and maximizes the time spent together—a gift in itself during the holidays.
Virtual Gatherings with AI-enhanced Experiences
For families who can’t be together in person, AI-driven tools offer creative ways to celebrate virtually. Video conferencing platforms now feature AI-powered transcription tools, which can support family members with hearing impairments. VR technology, although still emerging, enables families to gather around a “virtual” Thanksgiving table, creating a more immersive experience than a standard video call.
AI-enhanced filters and backgrounds add a festive touch to virtual gatherings, helping to recreate the Thanksgiving atmosphere digitally. For those separated by time zones, AI can automatically suggest the best times for video calls, ensuring everyone can join in on the celebration, whether they’re sharing stories or passing along family recipes. In this way, AI makes virtual Thanksgivings feel more intimate and connected.
Smart Shopping and the AI-Driven Black Friday Experience
For many, Thanksgiving is also the gateway to Black Friday shopping, a tradition that has evolved dramatically in recent years. AI has reshaped this experience, enabling hyper-personalised shopping recommendations, real-time stock updates, and even smarter supply chains that prevent the dreaded “out of stock” message.
AI can now predict which items are likely to be popular and adjust inventory levels to meet demand. This not only makes shopping more efficient but also reduces waste by helping retailers avoid overstocking. AI-driven online shopping platforms provide personalised deals based on browsing history and purchasing patterns, allowing shoppers to find just what they need without the rush of crowds. For consumers, it’s a streamlined, stress-free way to kick off the holiday season.
AI in Entertainment: Games, Movies, and More for Thanksgiving Fun
Entertainment is central to Thanksgiving celebrations, from family movie nights to board games. AI-driven platforms like Spotify and Netflix offer curated playlists and movie recommendations tailored to everyone’s tastes, keeping the whole family entertained. For instance, AI can suggest holiday classics or even new family-friendly releases based on user preferences, setting the perfect mood for Thanksgiving evening.
Additionally, interactive gaming systems with AI components allow multiple devices to sync up, making it easy for family members to play together, whether they’re in the same room or across the country. With AI in entertainment, Thanksgiving becomes a richer, more engaging experience, tailored to bring families together and create lasting memories.
A New Kind of Thanksgiving with AI
In many ways, AI is adding depth to Thanksgiving traditions, blending the familiar with the innovative. It’s not replacing the warmth and connection of the holiday but rather enhancing it—making meals more inclusive, travel less stressful, virtual gatherings more connected, shopping smarter, and entertainment more enjoyable. As AI continues to advance, it will play an even greater role in shaping how we celebrate and connect during holidays, no matter the distance.
Comment and Share:
So, this Thanksgiving, as families sit down for a meal, shop for deals, or tune into a movie, they’ll have AI quietly working in the background, enhancing their holiday experience in ways they might not even realise. The question for next year, perhaps, is how else AI might help us cherish and connect with loved ones. How will AI transform your holiday traditions in the years to come? Subscribe for updates on AI and AGI developments and share your thoughts in the comments below!
- You may also like:
- Shopping gets a Glow Up! Google’s AI Upgrades Transform the Game
- AI Chef: How ChatGPT Created a Smash Hit Pizza
- How AI Could Uncover the Mysteries of Haunted Houses
- Or try out RecipeGPT.io, an AI-powered recipe generator where you can enter ingredients or dietary restrictions by tapping here
Author
Discover more from AIinASIA
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

The Dirty Secret Behind Your Favourite AI Tools

How To Teach ChatGPT Your Writing Style

Upgrade Your ChatGPT Game With These 5 Prompts Tips
Trending
-

 Life3 weeks ago
Life3 weeks ago7 Mind-Blowing New ChatGPT Use Cases in 2025
-

 Learning2 weeks ago
Learning2 weeks agoHow to Use the “Create an Action” Feature in Custom GPTs
-

 Business3 weeks ago
Business3 weeks agoAI Just Killed 8 Jobs… But Created 15 New Ones Paying £100k+
-

 Learning2 weeks ago
Learning2 weeks agoHow to Upload Knowledge into Your Custom GPT
-

 Learning2 weeks ago
Learning2 weeks agoBuild Your Own Custom GPT in Under 30 Minutes – Step-by-Step Beginner’s Guide
-

 Life2 days ago
Life2 days agoHow To Teach ChatGPT Your Writing Style
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoAdrian’s Arena: Stop Collecting AI Tools and Start Building a Stack
-

 Life3 weeks ago
Life3 weeks agoAdrian’s Arena: Will AI Get You Fired? 9 Mistakes That Could Cost You Everything





















